How to Install Solar Panels on a Flat Roof
How to Install Solar Panels on a Flat Roof

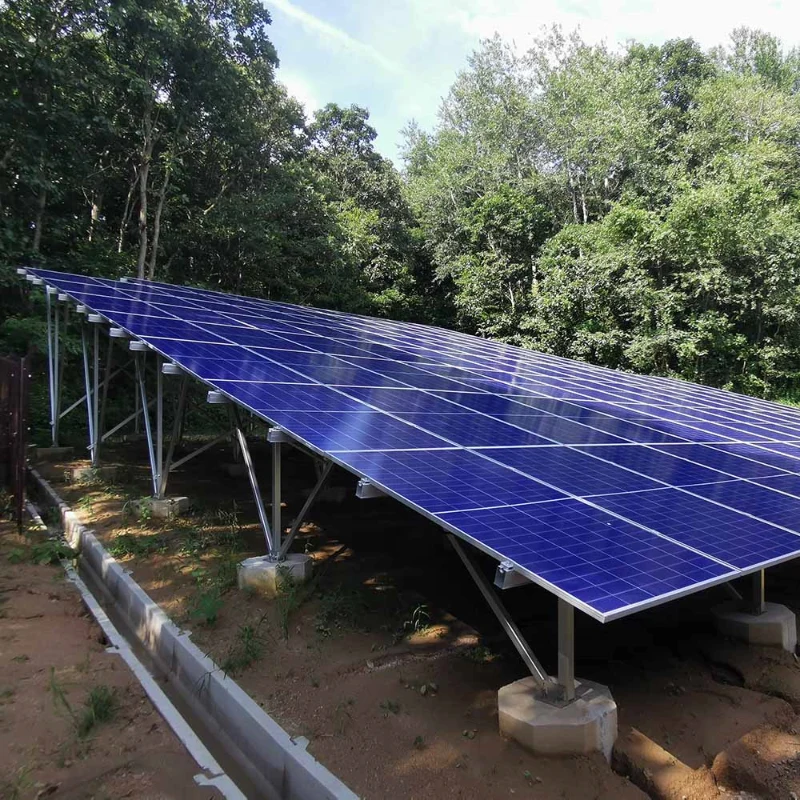
Installing solar panels on a flat roof is a viable and effective option for both residential and commercial solar systems. While most domestic properties in the UK have sloping or pitched roofs, there are still many homes and buildings with flat roofs—often in extensions, garages, garden rooms, or even on larger apartment blocks.
Why Install Solar Panels on a Flat Roof?
The most obvious reason for installing solar panels on a flat roof is simply the lack of a pitched roof. However, there are other benefits and scenarios where a flat roof may be the best option for solar:
1.Limited Roof Space: If your main roof faces north or has shading issues, installing solar panels on a flat roof or outbuilding can help maximize sunlight exposure.
2.Shading Issues: If your home's primary roof is shaded during part of the day, adding solar panels to a flat surface away from the shadows can boost your energy generation.
3.Living in a Flat or Apartment: In urban environments, solar panels can be installed on the roofs of apartment buildings or high-rise flats. While this may be a more complex project—especially if you rent or share the building—it remains a highly effective option.
How to Install Solar Panels on a Flat Roof
There are several mounting systems available for installing solar panels on flat roofs, each with different methods of securing the panels and adjusting their angle. Here are a few common options:
Mini Rail Systems
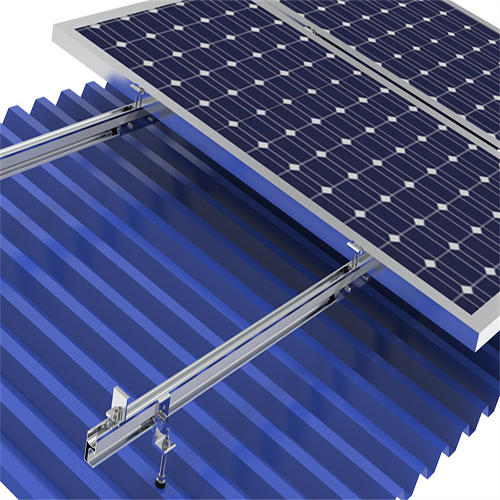
Mini rail systems are ideal for lightweight roofs and are often used with box-section metal roofs. These systems typically involve self-tapping screws that secure the rails to the roof. Each rail usually holds one or two panels, but larger arrays can use additional mid-fixings.
Advantages:
Cost-effective and simple to install
Suitable for roofs with lower load-bearing capacity
Minimal maintenance required, but less efficient at self-cleaning when the panels lie flat
Disadvantages:
Panels may sit at a shallow angle or even flat, leading to less effective rainwater cleaning.
2. A-Frame Systems
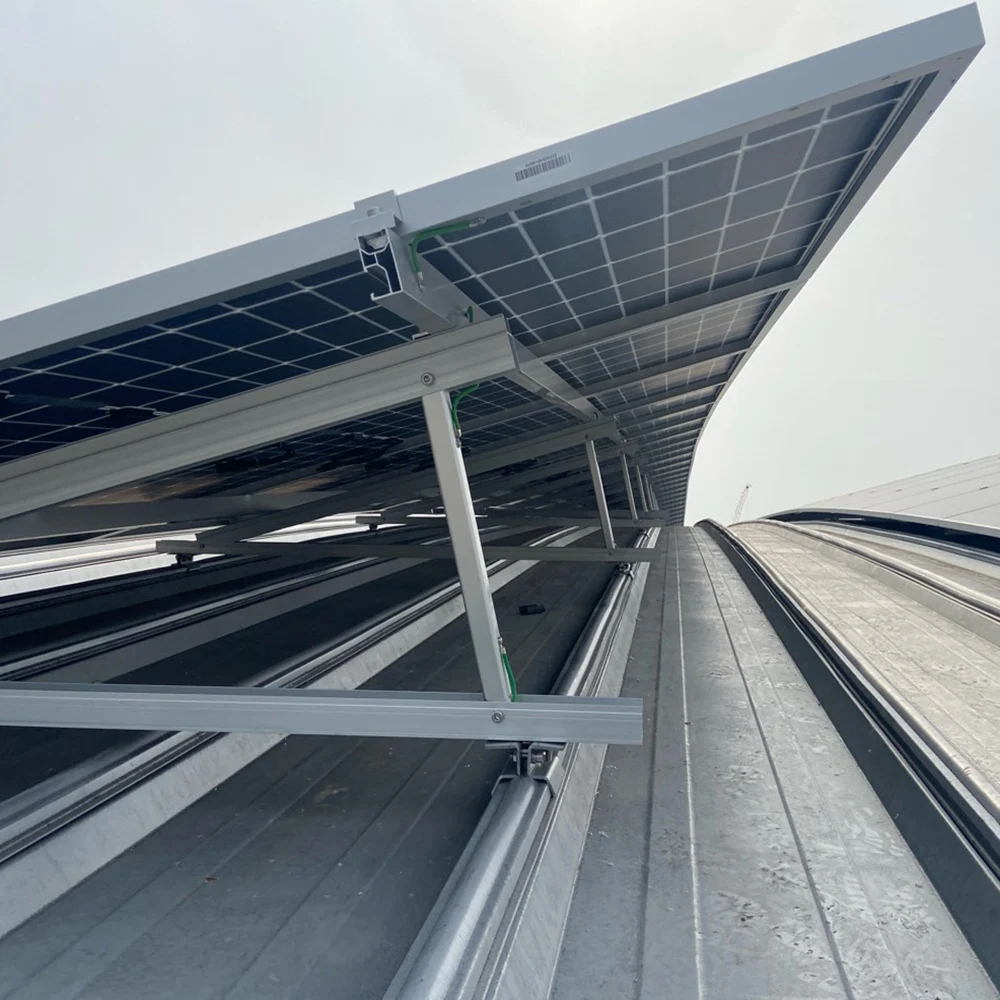

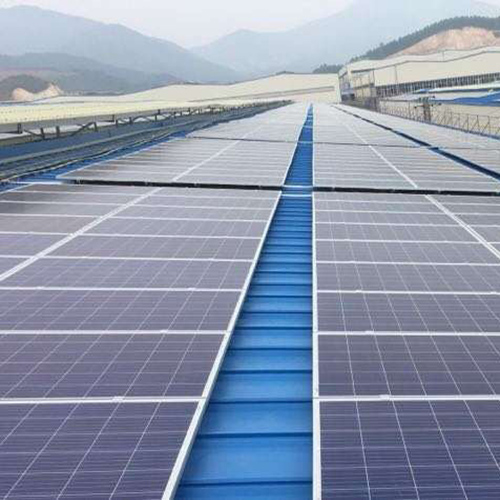
A-frame systems are the most popular choice for mounting solar panels on flat roofs. These frames can be bolted to the roof, weighted down with ballast, or tethered to ground anchors. A-frames allow you to set the panels at the optimal angle for maximum sun exposure.
Advantages:
1.Panels are angled to capture sunlight efficiently and benefit from natural self-cleaning from rain
2.Versatile and adjustable
3.More expensive than mini rails but much more effective
Disadvantages:
Higher cost and more installation work
Requires more space on the roof
3. Tubs
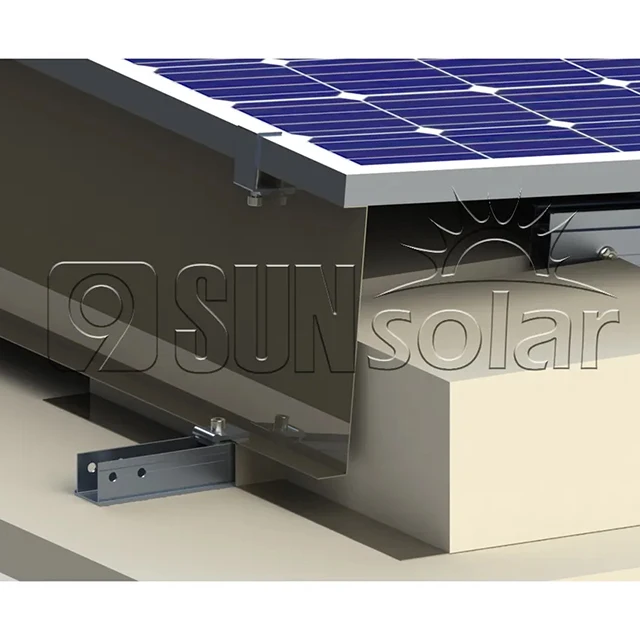

A simpler, more portable solution involves mounting the solar panels on "tubs"—containers (usually made from plastic or metal) filled with sand or water to provide ballast. The panels are secured at the angle the tub is designed for, offering flexibility in installation.
Advantages:
1.Easy to transport and install
2.Lightweight and simple to adjust
3.Suitable for use on both flat roofs and open ground installations
Disadvantages:
Requires ample space for the tubs and may be less secure in very windy conditions
4. Angled Systems for East and West-Facing Panels
One of the benefits of flat roofs is that they allow for flexible panel orientation. You can mount the panels at any angle and point them in different directions—such as east or west—to capture more sunlight throughout the day.
East/west-facing systems are especially advantageous because they can generate up to 30% more power compared to a traditional south-facing setup, as they take advantage of sunlight during the morning and afternoon.
Advantages:
1.Can increase energy yield by up to 30% compared to south-facing arrays
2.Panels are supported by each other, making them more stable in windy conditions
Disadvantages:
May require more panels to achieve the same level of energy generation as a south-facing system
The Best Angle for Solar Panels on Flat Roofs
Flat roofs offer the unique advantage of being able to choose the optimal angle for solar panels. While the ideal angle for solar panels generally falls between 30 to 40 degrees, this can vary depending on your location and the orientation of your panels.
In the UK, most pitched roofs are between 20 and 50 degrees, which is often ideal for solar panels. If your roof is steeper or shallower than this, adjusting the angle on a flat roof can help optimize panel efficiency.
Benefits of Installing Solar Panels on a Flat Roof
There are several advantages to mounting solar panels on a flat roof:
Flexibility with Panel Placement: You have greater control over the angle and orientation of your panels, which allows you to optimize energy production, particularly with no risk of shading from other parts of the roof.
Room for More Panels: Flat roofs generally offer more space, allowing you to fit more panels, including less efficient (and typically cheaper) models. This can reduce upfront costs while still generating enough electricity.
Less Visual Impact: Solar panels installed on a flat roof are often less visible from the ground, making them a discreet option for homeowners concerned with aesthetics.
Easy Installation and Maintenance: Flat roofs provide easy access, which simplifies installation and ongoing maintenance, including cleaning.
Self-Cleaning Benefits: Because flat roofs allow you to angle the panels, rainwater can naturally wash away dirt and debris, improving efficiency without the need for manual cleaning.
Disadvantages of Installing Solar Panels on a Flat Roof
While there are many benefits, there are a few challenges to consider:
Roof Load Capacity: Flat roofs may not be designed to bear the weight of solar panels and mounting systems, so proper calculations are necessary to ensure the roof can support the added load.
Space Requirements: Unlike pitched roofs, where panels can be mounted close together, panels on flat roofs need to be spaced to prevent shading. This means flat roof installations can take up more space.
Wind Resistance: If not properly secured, solar panels on a flat roof may be more susceptible to wind damage, especially in areas prone to high winds. This can be mitigated by using weighted systems like ballast or tethering panels securely.




